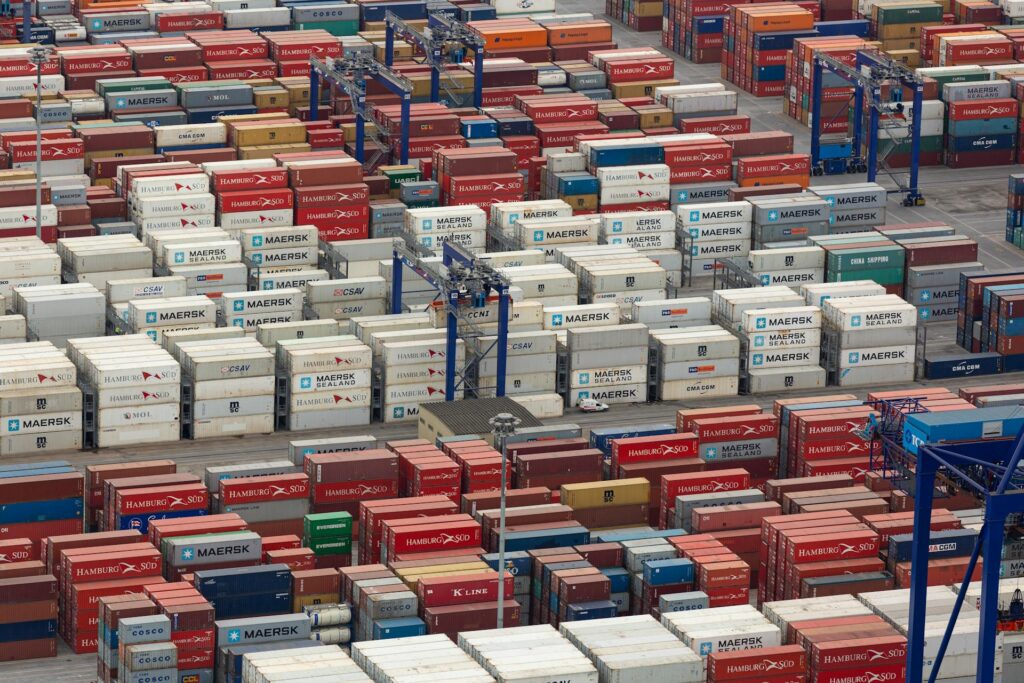
In today’s global trade landscape, sea freight serves as the backbone of international logistics, facilitating the transportation of vast quantities of goods around the world. Germany, as one of the core engines of the European economy, conducts extensive trade with countries across the globe, and its sea freight business is particularly busy and complex. Understanding the knowledge of sea freight to Germany is of crucial importance, whether for enterprises planning to expand overseas markets or for practitioners engaged in international trade.
This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of the types of containers involved in sea freight to Germany, the categories of goods that can be transported, as well as the detailed transportation processes for various goods, helping you comprehensively grasp the key points in this critical field.
I. Types of Containers for Sea Freight to Germany
- General Purpose Container (GP)
- Dimensions: Commonly available in two specifications, 20 feet and 40 feet. A 20-foot container is approximately 6 meters long, 2.2 meters wide, and 2.3 meters high; a 40-foot container is about 12 meters long, with the same width and height as the 20-foot one.
- Usage: It is suitable for transporting most dry cargoes, such as machinery parts, furniture, and ordinary electronic products that are non-hazardous. It can easily accommodate these goods and is widely used in sea freight to Germany, being the top choice for regular cargo transportation.
- Capacity: The theoretical volume of a 20-foot container is about 30 cubic meters, but the actual usable volume is roughly 25 – 27 cubic meters; the theoretical volume of a 40-foot container is approximately 60 cubic meters, and the actual usable volume is around 55 – 57 cubic meters.
- 40-foot High Cube Container (HC)
- Usage: Primarily designed for goods with larger volumes but relatively lighter weights, like textiles and plastic products. It is taller than the ordinary 40-foot container, providing ample space for such goods.
- Capacity: The theoretical volume is about 73 cubic meters, and the actual usable volume is approximately 68 – 70 cubic meters.
- Open Top Container
- Usage: Specifically used for transporting overheight cargoes or those that need to be loaded from above, such as heavy machinery and steel products. Its top can be opened, facilitating the loading and unloading of large equipment.
- Reefer Container
- Usage: For perishable food items, such as fresh fruits, meat, and pharmaceuticals with strict temperature requirements, the reefer container can provide a precisely controlled temperature environment to ensure the quality of the goods remains intact during transportation.
- Flat Rack Container
- Usage: Suitable for transporting overlength, overwidth, and irregularly shaped cargoes, like steel pipes and large mechanical equipment. It has no top and side walls, making it convenient for placing and securing the cargo.
- Bulk Container
- Usage: Mainly used for transporting grains, powdered, or granular goods, enabling efficient transportation of such commodities.
II. Types of Goods for Sea Freight to Germany
- General Cargo
General cargo accounts for a significant portion in sea freight to Germany. It includes various machinery products, furniture, plastic products, textiles, and ordinary electronic products (such as household appliances without batteries and ordinary lamps, etc.). These goods are relatively safe during transportation, do not require special transportation conditions and regulatory requirements, and the transportation process is relatively straightforward. - Sensitive Cargo
The transportation of sensitive cargo is relatively more complicated.- Food Products: This category encompasses all kinds of processed foods, beverages, and condiments. When transporting food, it is necessary to ensure the packaging of the goods is intact and complies with hygiene standards. At the same time, relevant food inspection and quarantine certificates need to be provided to meet the strict requirements of German customs regarding food safety.
- Electronic Products: Here, it mainly refers to electronic products with batteries, such as mobile phones, laptops, and power banks. Due to the potential safety risks associated with batteries, specific packaging requirements must be followed during transportation, and relevant safety certification documents for the batteries, such as UN38.3 test reports, need to be provided. Additionally, different types of batteries (such as lithium batteries and lead-acid batteries) have different transportation regulations.
- Cosmetics: This includes skin care products, makeup, and perfumes. Cosmetics usually contain chemical components, so accurate ingredient declaration is required, and some products may even need toxicity tests. For perfumes and other cosmetics containing alcohol, the transportation requirements are even more stringent.
- Pharmaceuticals: The transportation of pharmaceuticals is strictly regulated. Firstly, the goods must be legally and compliantly produced, and the shipper needs to provide relevant documents such as the production license and drug registration certificate. During transportation, it is essential to ensure that the storage conditions of the drugs meet the requirements, such as temperature and humidity. Meanwhile, German customs have detailed regulations regarding the import of pharmaceuticals, and it is necessary to understand and prepare the corresponding customs clearance documents in advance.
III. Transportation Processes for Various Goods in Sea Freight to Germany
- Transportation Process of General Cargo
- Booking: The shipper applies for shipping space to the freight forwarder or shipping company according to the volume, weight, and transportation time requirements of the goods, providing detailed information about the goods, such as the name, quantity, packaging form, port of departure, and port of destination. The freight forwarder or shipping company arranges suitable containers and sailing schedules based on this information.
- Cargo Packing: After the booking is successful, the shipper transports the goods to the designated packing location. The shipper can choose to pack the goods by themselves or entrust the freight forwarder to arrange the packing service. When packing, attention should be paid to the placement and fixation of the goods to ensure that they do not move or get damaged during transportation. Meanwhile, the packing list should be accurately filled out to record the detailed information of the goods in the container.
- Export Customs Clearance: The shipper or the freight forwarder entrusted by the shipper prepares the necessary documents for customs declaration, such as commercial invoices, packing lists, customs power of attorney, and contracts, and submits them to the customs at the port of export. The customs will inspect the goods to verify whether the information of the goods is consistent with the declared content. If the inspection is passed, the goods will be released.
- Shipment: After the goods are released by the customs, dock workers load the containers onto the designated ships. The ships then sail to the German port of destination along the predetermined route. During transportation, the shipper can track the transportation status of the goods in real-time through the cargo tracking system provided by the freight forwarder or shipping company.
- Import Customs Clearance: After the goods arrive at the German port of destination, the consignee or the freight forwarder entrusted by the consignee needs to carry out import customs clearance with the German customs. Relevant documents such as bills of lading, commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin need to be submitted. After the customs verifies and approves, corresponding tariffs, value-added taxes, and other taxes will be levied. If the goods need to be inspected, the customs will arrange the inspection, and the goods can be released only after passing the inspection.
- Delivery: After completing the import customs clearance procedures, the consignee can pick up the goods at the dock or the designated warehouse. If the consignee requires the freight forwarder to provide door-to-door delivery service, the freight forwarder will arrange vehicles to transport the goods to the designated receiving address.
- Transportation Process of Sensitive Cargo (Taking Electronic Products as an Example)
- Preliminary Preparation: The shipper must first identify that the goods belong to the category of sensitive electronic products, especially those with batteries. Select a freight forwarder with rich experience in transporting sensitive cargo and consult them about the transportation requirements and precautions. Prepare relevant declaration materials, such as sea freight booking notes, MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) of the goods, UN38.3 test reports (for dangerous goods such as lithium batteries).
- Booking and Packaging: Submit a booking application to the freight forwarder or shipping company, specifically indicating that the goods are electronic products with batteries and informing them of the special attributes and requirements of the goods. In terms of packaging, use packaging materials that meet the regulations to properly protect the electronic products from collisions and damages during transportation. At the same time, clearly mark the name, model, quantity, weight, and other information of the goods on the packaging and attach corresponding warning labels, such as the dangerous goods label for lithium batteries.
- Export Customs Clearance: Similar to the customs clearance of general cargo, but due to the sensitive nature of the goods, the customs declaration materials need to be more detailed and accurate. In addition to the regular customs declaration documents, MSDS, UN38.3 test reports, and other supporting documents need to be provided. When the freight forwarder or customs broker declares to the customs at the port of export, it is necessary to ensure that the declared content is completely consistent with the actual situation of the goods to avoid the goods being detained or delayed due to inaccurate declaration.
- Shipment: After the goods are released by the customs, they are shipped. During transportation, close attention should be paid to the ship’s movements and the status of the goods. Since electronic products with batteries pose certain risks during transportation, the freight forwarder or shipping company may take some special transportation measures, such as strengthening the fixation of the containers and monitoring the temperature and humidity of the transportation environment.
- Import Customs Clearance: After the goods arrive at the German port of destination, the consignee or the freight forwarder entrusted by the consignee conducts import customs clearance with the German customs. In addition to submitting the regular customs clearance documents, relevant certification documents for the goods, such as CE certification (European Conformity marking certifying compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards in the EU), need to be provided. The German customs will conduct a strict inspection of the goods, not only checking the quality and quantity but also verifying whether the goods meet the German safety and environmental protection standards. If there are any problems with the goods, they may be required to be rectified or returned.
- Delivery and Follow-up: After completing the import customs clearance procedures, the consignee picks up the goods. If the goods are damaged or lost during transportation, the consignee should promptly contact the freight forwarder or insurance company and follow the relevant procedures for claiming compensation.
In conclusion, sea freight to Germany involves numerous links and key points. Whether it is the precise selection of containers, the proper identification of cargo types, or the strict adherence to the transportation process, practitioners need to be extremely vigilant to ensure that the goods reach their destinations smoothly and achieve seamless international trade. It is hoped that this scientific article can serve as a guiding light for you in the complex yet full-of-opportunities field of sea freight to Germany.