In today’s globalized era, cross – border e – commerce is booming, and the international shipment of personal items between individuals is also becoming increasingly frequent. However, the cross – border transportation of small – capacity lithium batteries in phones, laptops, etc., has become a headache for many people. These seemingly ordinary’small batteries’ can cause a series of ‘big troubles’ in cross – border transportation. Now, let’s delve into the relevant knowledge of cross – border battery transportation for phones and laptops to help you comply with customs regulations, avoid risks and losses.
I. Introduction: The Ubiquitous ‘Dangerous Goods’
1. Starting with a Case
Once upon a time, a cross – border e – commerce seller, in order to send a batch of phone batteries to a foreign warehouse before the sales peak season, chose a seemingly affordable logistics channel. Without in – depth understanding of the battery transportation rules, he simply packed the batteries and sent them out. As a result, the parcels were detained by customs during transportation. Not only were the goods returned, but the seller also missed the sales peak season of the store, suffering heavy losses. This case fully illustrates that if small batteries are not handled properly in cross – border transportation, they can easily turn into big problems.
2. Revealing the Contradiction
In our daily lives, the batteries in phones, laptops and other devices are very safe, bringing great convenience to our lives and work. However, in the transportation process, these batteries are regarded as ‘dangerous goods’. This is because during transportation, if lithium batteries are squeezed, collided, or short – circuited, they may catch fire or explode. Moreover, lithium batteries have relatively active chemical properties and are prone to thermal runaway under certain conditions, leading to safety accidents. Therefore, to ensure transportation safety, strict regulations have been formulated internationally for the transportation of lithium batteries.
3. The Value of This Article
By reading this article, you will clearly understand the rules and requirements for the cross – border transportation of small – capacity lithium batteries in phones, laptops, etc. It can help you avoid returns, fines and other issues caused by battery transportation problems, ensure the safety of goods transportation, and guarantee the smooth customs clearance of goods, making your cross – border e – commerce business or personal shipments more seamless.
II. Basics: Recognize the Battery in Your Hand
1. Identity Definition
Pure Batteries
Pure batteries refer to batteries, power banks, etc. that are mailed separately. These batteries are not installed in devices and are in an independent state. For example, some sellers will mail phone batteries separately to meet customers’ needs for battery replacement. Many people also buy power banks as backup power sources. In cross – border transportation, these separate batteries and power banks all fall into the category of pure batteries.
Battery – containing Products
Battery – containing products refer to devices with installed batteries, such as phones, laptops, tablets, etc. The batteries in these devices are integrated with the devices and are transported in the form of the devices. For instance, the battery in our daily smartphones provides power for the phone. When we transport the phone across borders, it is a battery – containing product.
Key Differences
The transportation rules and restrictions for pure batteries and battery – containing products are significantly different. Since pure batteries are not protected by devices, they are more vulnerable to external factors during transportation, so their transportation requirements are more stringent. Battery – containing products, on the other hand, are relatively less risky in transportation because of the protection of the device’s shell, but they also need to follow certain rules.
2. Core Concept: The ‘Watt – hour (Wh)’ You Must Know
Simple Explanation
Watt – hour (Wh) is a unit for measuring battery energy. Its calculation formula is simple: Wh = V * Ah, where V represents the battery voltage and Ah represents the battery ampere – hour capacity. For example, if a battery has a voltage of 3.7V and an ampere – hour capacity of 2Ah, its watt – hour is 3.7 * 2 = 7.4Wh.
Finding and Calculating
On our phone and laptop batteries, the relevant battery parameters are usually marked. Some batteries will directly indicate the watt – hour value, and we can check it directly. If the watt – hour value is not marked, we can calculate it according to the voltage and ampere – hour capacity marked on the battery using the above formula. For example, if we see that the voltage marked on a phone battery is 3.85V and the ampere – hour capacity is 4500mAh (converted to Ah is 4.5Ah), then its watt – hour is 3.85 * 4.5 = 17.325Wh.
Defining the Boundary
In international transportation rules, 100Wh is an important threshold for most transportation methods. Generally, batteries with a watt – hour less than 100Wh have relatively fewer restrictions in transportation, but they still need to meet certain conditions. Batteries with a watt – hour greater than 100Wh require more strict approval and special transportation arrangements.
III. Restrictions: The ‘Tightening Spell’ of Quantity and Capacity
1. Restrictions for Personal Shipments / General Cargo Channels
Air Freight
In terms of air freight, ordinary postal channels (such as China Post, Hong Kong Post Small Packet) usually strictly restrict the mailing of pure batteries. This is because the air transportation environment is special, and the safety requirements for goods during flight are extremely high. Once a pure battery causes a danger during transportation, it may pose a serious threat to the safety of the aircraft. Therefore, to ensure flight safety, these ordinary postal channels generally do not accept the mailing of pure batteries.
Sea Freight
Sea freight is relatively more lenient in battery transportation restrictions, but it also has strict packaging and declaration requirements. The transportation time of sea freight is long, and during transportation, the batteries may be affected by seawater humidity, bumps, etc. So, batteries for sea freight must be properly packed to prevent short – circuits during transportation. At the same time, relevant battery information, including battery type, quantity, watt – hour, etc., must be accurately declared.
2. Permissible Scope for Commercial Channels / Dangerous Goods Channels
Pure Batteries
For lithium – ion batteries, the rated watt – hour usually requires ≤ 20Wh (applicable to phone batteries, etc.). Moreover, when transporting pure batteries through commercial channels, there are clear single – ticket / single – piece quantity restrictions. Different transportation companies and channels may have different quantity restrictions. For example, some channels stipulate that a single ticket can transport a maximum of 10 phone batteries.
Battery – containing Products
The batteries in devices usually require a rated watt – hour ≤ 100Wh (applicable to most laptops and tablets). The restrictions on the number of battery – containing devices are relatively more lenient, but they also need to be determined according to the specific transportation situation and channel. For example, some channels do not have a strict upper limit on the number of battery – containing devices transported simultaneously, but they require reasonable packaging and fixing of the devices.
Spare Batteries
When transporting devices with spare batteries, there are also special regulations. Generally, spare batteries must be carried with you or specially packed. If you carry spare batteries with you, they need to be placed in a container that meets safety requirements and cannot exceed a certain quantity. If they are transported through special packaging, they need to be operated in accordance with relevant packaging requirements to ensure the safety of spare batteries during transportation.
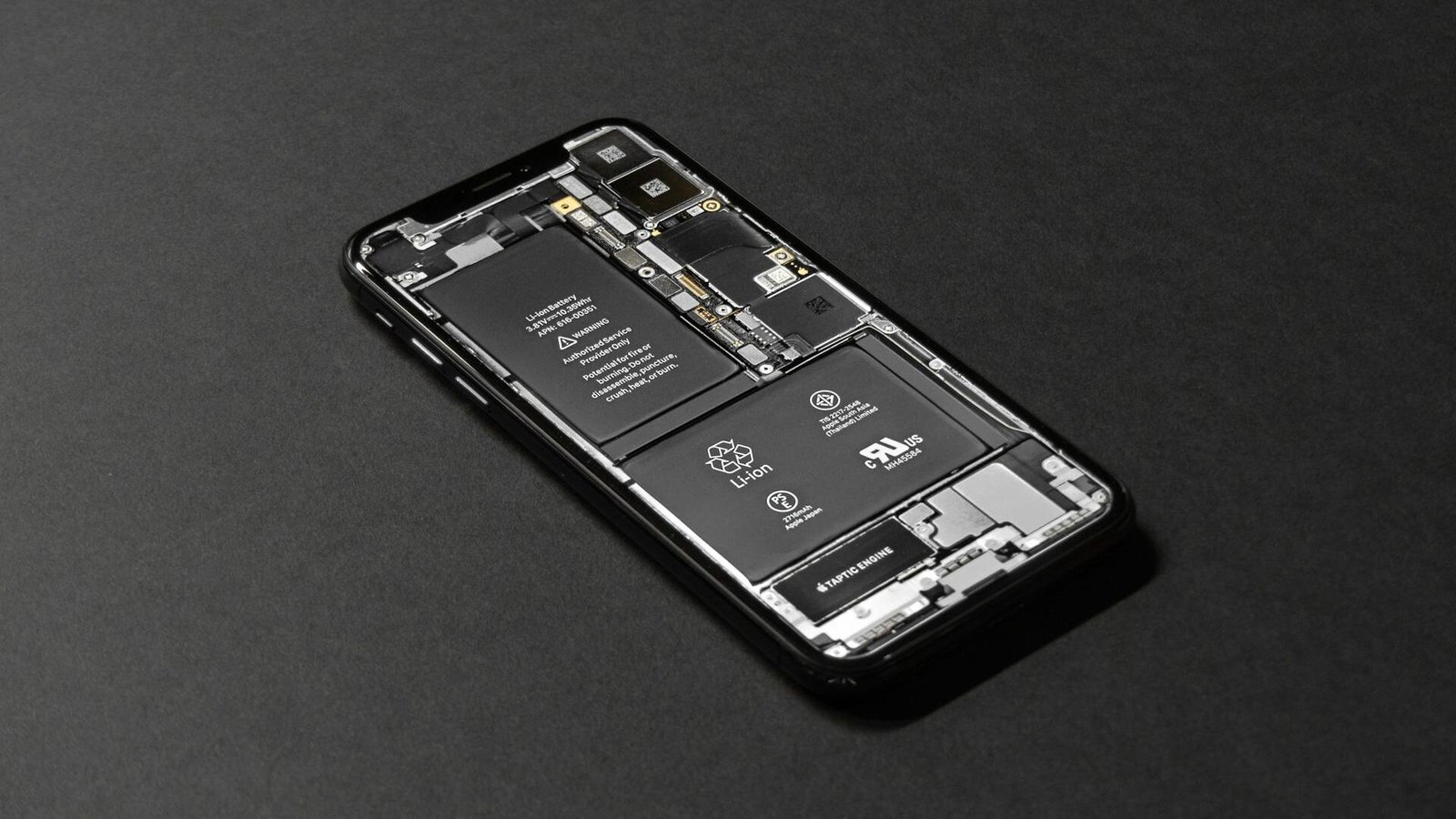

IV. Practical Guide: Armor the Battery with ‘Explosion – Proof Gear’
1. Core Principle
The core principle of battery packaging is foolproof insulation and short – circuit prevention. This is because if a battery is short – circuited during transportation, it may cause a fire or explosion. Therefore, when packaging batteries, effective measures must be taken to ensure the insulation performance of the battery and prevent the positive and negative electrodes of the battery from contacting.
2. Three – Step Packaging Method
Step 1: Individual Insulation
Each battery must be independently encapsulated to prevent mutual contact. The correct way is to use the original retail packaging, individual plastic bags, and bubble wrap to completely wrap the battery. For example, for a phone battery, it can first be placed in the original packaging box, then sealed with a plastic bag, and finally wrapped with bubble wrap. The wrong way is to throw multiple batteries directly into a box, which may cause the batteries to squeeze and collide with each other, leading to short – circuits.
Step 2: Fixing and Buffering
Fix the insulated battery in the middle of the packaging box to ensure it doesn’t move or collide. Appropriate fillers (such as bubble pads, foam) can be used to fill the packaging box to keep the battery stable inside. For example, when packaging a laptop, bubble pads can be filled around the computer to prevent it from shaking during transportation, thus protecting the battery from damage.
Step 3: Outer Box and Labeling
Use a sufficiently sturdy outer box to package the battery and the device. The outer box must be able to withstand a certain amount of pressure and collision to protect the internal battery and device. On the outer box, a lithium – battery label (Lithium Battery Mark, which must be diamond – shaped and in compliance with size requirements) and a contact information label (“Please contact XXX for disposal”) must be pasted.
The lithium – battery label allows transporters and customs officers to clearly know that there are lithium batteries inside, facilitating the adoption of corresponding safety measures. The contact information label is for timely contact with relevant personnel in case of special situations. It should be noted that do not paste the wrong “Cargo Aircraft Only” label (only applicable in specific situations), as incorrect pasting may lead to misunderstandings and troubles during transportation.
3. Illustrations of Common Packaging Failure Cases
To give everyone a more intuitive understanding of incorrect packaging methods, we can use simple drawings or pictures to show some common failure cases. For example, pasting tape directly on the electrodes will damage the battery’s insulation performance and easily cause a short – circuit. Another example is placing the battery casually in a cardboard box without any fixing or buffering, which may cause the battery to be severely collided and squeezed during transportation. Through the display of these cases, everyone can better avoid similar mistakes when packaging batteries.
V. Platform Rules: The ‘House Rules’ of Cross – Border E – commerce
1. Amazon (FBA)
When selling battery – containing products on the Amazon (FBA) platform, you must provide an MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) and a UN38.3 test report. The MSDS can provide detailed information about the battery, including chemical composition and safety precautions. The UN38.3 test report proves that the battery has passed a series of safety tests and meets international transportation requirements. In addition, Amazon has additional specific requirements for battery labels and packaging. For example, the battery label must clearly indicate the battery type, watt – hour, etc. The packaging must comply with Amazon’s regulations to ensure the safety of the battery during transportation and storage.
2. AliExpress / Shopify, etc.
Platforms like AliExpress and Shopify remind sellers to choose officially recognized ‘battery channels’ or’special freight forwarders’. These channels and freight forwarders have professional transportation capabilities and experience and can better handle battery transportation issues. At the same time, these platforms clearly prohibit the mailing of pure batteries through the platform’s general shipping lines. If sellers violate the regulations, they may face penalties from the platform, such as sales restrictions and fines.
3. Summary
Before selling battery – containing products on a platform, be sure to check its latest logistics policies. Since the policies of different platforms and at different times may change, only by keeping up – to – date with the latest policies can you ensure that your sales and transportation activities comply with regulations and avoid unnecessary risks and losses.
VI. Summary and Action Checklist
1. Review of Core Points
When transporting phone and laptop batteries across borders, we should first confirm the battery’s identity (pure battery / battery – containing product), then check the battery’s energy (Wh), and finally do a good job in packaging (insulation + labeling). These three steps are the keys to ensuring the smooth transportation of batteries.
2. Pre – shipment Self – check List
Before sending a shipment, we can conduct a self – check according to the following list:
- I have confirmed the battery type and watt – hour.
- I have selected the correct and recognized transportation channel.
- Each battery has been independently insulated.
- The packaging box is fully filled, and the battery will not shake.
- The outer box has correctly pasted the lithium – battery label and contact label.
- All required documents (such as invoices, declarations) are ready.
3. Final Reminder
When you are unsure about the cross – border battery transportation rules, be sure to consult a professional logistics service provider and do not take chances. Professional logistics service providers have rich experience and professional knowledge and can provide us with accurate information and advice to help us avoid losses caused by transportation problems.
In cross – border transportation, small – capacity lithium batteries in phones, laptops, etc., may seem insignificant, but they can bring a lot of trouble. It is hoped that through the introduction of this article, it can help cross – border e – commerce sellers and individual shippers better understand the rules and requirements of cross – border battery transportation and successfully complete the transportation of goods.